Every business relies on nature for resources and ecosystem services such as water, food, fiber, minerals, pollination of crops, water filtration and climate regulation, both in their own operations and supply chains, and for their employees and customers.
But nature is at a tipping point. The natural materials and ecosystem services – that we all rely on and that also power businesses – are under massive strain. Without transformative changes in our economy and the way we do business, nature-negative trends such as global declines in species populations as well as losses in efficiency and efficacy of ecosystem service provision are expected to continue through to 2050 and beyond. Under current scenarios, over half of the world’s total GDP is at moderate or severe risk due to nature loss. The role of business is critical to delivering a nature positive world by 2030. Building on existing commitments and actions related to nature, businesses should aim to halt and reverse negative impacts on nature and then should aim for their positive impacts to outweigh their negative ones in the same eco-regions or in similar types of ecosystems.
Nature consists of the natural, physical and material world around us, including the air we breathe, the water we drink, the forests, land and oceans we rely on. When we talk about nature, we are focusing on the natural resources, ecosystem services and biodiversity on which livelihoods and economies depend, such as food, fiber, minerals, pollination, water filtration, climate regulation and disease control, but also recreation and well-being.
Nature includes biodiversity which underpins the health, abundance and resilience of our natural resources and ecosystems. We recognize that biodiversity loss is a significant component of nature loss overall.
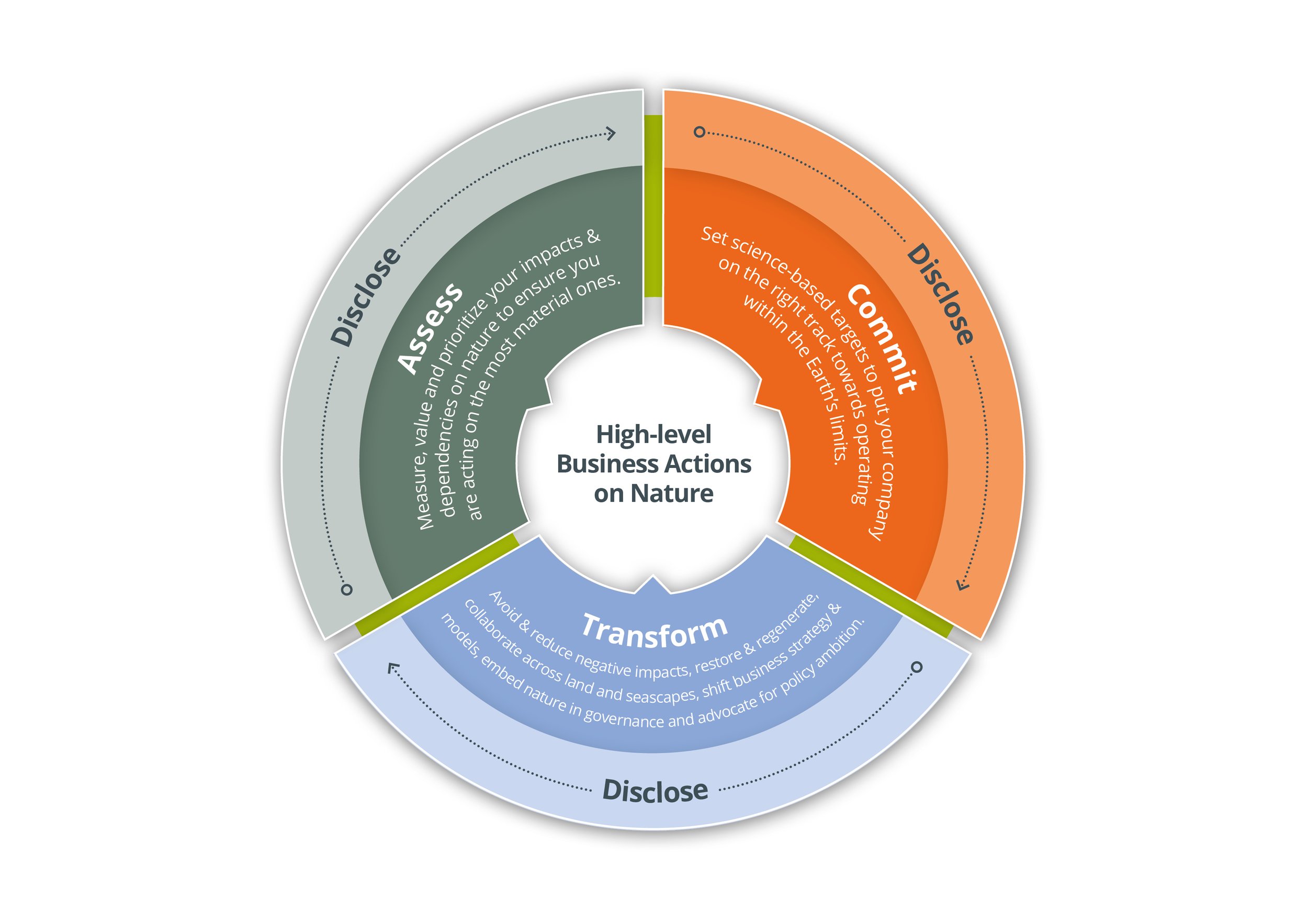
These high-level business actions provide companies with the key actions they can take to signal that they are making meaningful contributions to help reverse nature loss and contribute to an equitable, nature-positive world, where positive impacts outweigh negative ones.
Businesses that have started on their nature journey should think through how to develop a credible nature strategy to deliver concrete long-term actions to halt and reverse nature loss. As part of Business for Nature’s campaign ‘It’s Now for Nature’, use the Nature Strategy Handbook developed in collaboration with PwC. The handbook includes guiding questions and resources to show what would be expected from a publicly disclosed nature strategy. Once your nature strategy is ready and approved, we encourage you to upload it onto the website and share it publicly as part of the campaign.
A note on alignment: These actions have been developed in collaboration with leading organizations. They build on existing action frameworks and guidance, including the Natural Capital Protocol, Science Based Targets Network's target-setting guidance, World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD) Roadmaps to Nature Positive: Foundations for All Businesses, Taskforce for Nature-related Financial Disclosures framework.
Measure, value and prioritize your impacts and dependencies on nature to ensure you are acting on the most material ones
Conduct an initial materiality assessment to prioritize efforts. Ensure you will be working on your most material impacts and dependencies on nature by performing materiality assessments across the production and consumption value chain - from extraction of raw materials to post-consumer waste. Using guidance from SBTN, TNFD’s LEAP process, and ENCORE, companies can identify and manage priority environmental impacts, dependencies, and locations. For example, you may realize that the biggest impact your company has is indirectly through freshwater use from your suppliers and/or consumers.
Measure and evaluate impacts and dependencies on nature. Build on your initial materiality assessment and conduct your own natural capital assessment by following the Natural Capital Protocol. Find the right tool to assess your impacts and dependencies through the Natural Capital Toolkit and where relevant, apply supplementary guidance on finance, biodiversity and food systems. Get in touch with We Value Nature to build your skills and capacity along your natural capital journey.
Assess risks and opportunities. From understanding your impacts and dependencies on nature to identifying and assessing your company’s nature-related risk. Use the guidance provided by the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) to show how your organization evaluates and manages nature-related risks and opportunities. Identify priority locations for target setting and action using tools like the Integrated Biodiversity Assessment Tool (IBAT) for Business and dig deeper into particular risks and opportunities you have identified, for example by using the WWF Risk Filter Suite.
Consider climate and people within your nature assessment. As you develop your approach to nature action, consider the relevance of climate and the just transition, and ensure you take an integrated approach wherever appropriate, for example by following Capitals Coalition’s Principles of Integrated Capitals Assessments. Consider the implications of your business and approach to nature for all stakeholder groups including indigenous people and local communities.
Set transparent, time-bound, specific, science-based targets to put your company on the right track towards operating within the Earth’s limits
Define ambition and goals. Provide an overview of the aspirations your business has to contribute to a nature positive world through aligning with the goals and targets of the Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) (to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030 and reach full recovery by 2050). Support this ambition by making meaningful, informed, and public commitments through credible platforms and identifying goals which will aid your business to achieve your ambition.
Set targets. Measure your baseline impacts and set measurable targets. These targets should relate to reducing your negative impacts and increasing your positive impacts by restoring ecosystems, including land, freshwater, and oceans, as well as responding to your nature-related risks and opportunities. Prepare to set science-based targets for nature using SBTN’s technical guidance, starting with freshwater and land, as well as for climate through the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi). Ensure that targets are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), and where possible, based on science, reflecting priority impacts and dependencies for your company, your region, and the planet. Be as ambitious as possible and aim to contribute to a nature positive world – alongside carbon neutrality – across your operations and value chains by 2030. Monitor, report and improve on progress towards commitments and targets.
Contribute to systems transformation by avoiding and reducing negative impacts, restoring, and regenerating, collaboration across land, seascapes and river basins, shifting business strategy and models, advocating for policy ambition and embedding your strategy within your corporate governance
Avoid and reduce. Prevent impacts from happening in the first place or eliminate the impact entirely. Do as much as possible to minimize impacts across your value chain when elimination is not possible.
Stop any damage in priority areas to have “zero harm” on biodiversity and nature, such as the Amazon rainforests and coral reefs, while simultaneously acting to draw down impacts across less-threatened landscapes and ecosystems. If you are aware of certain practices that harm biodiversity - e.g., the application of fertilizers and pesticides, use of ghost nets and bottom trawls, take immediate action to change them, even if you do not yet have perfect information.
While it is critical to address material impacts as soon as possible at landscape or seascape-level, many companies start by taking steps to motivate employees and lay the groundwork for further action. While more strategic decisions are discussed and made, in parallel you can start by making gestures such as switching to renewable energy sources, increasing water use efficiency, removing single-use plastics from the office, recycling waste, planting native and pollinator-friendly species, and installing nesting boxes for birds and bees in areas around your operations. However, be sure that these first steps lead to widespread action to address the most material impacts and dependencies across your value chain. Monitor and evaluate your progress to implement these actions.
Restore and regenerate. Actively work in collaboration with others within your operations and across value chains to restore ecosystems, including forests, soils, freshwater systems, and marine environments. Invest in nature-based, inclusive, and holistic solutions, which also capture carbon and improve livelihoods. The NBS benefits explorer is a great starting tool for companies who want to invest in nature-based solutions. Adopt best practices in context-based and collective stewardship by understanding local risks and opportunities and working with other local natural resource users (e.g., freshwater users in a landscape) and local authorities. Support enforcement of local community and indigenous rights, and respect Indigenous People’s right to Free, Prior and Informed Consent.
Follow the IUCN Global Standard for Nature-based Solutions which is a widely accepted reference that ensures a holistic approach is taken when using nature-based solutions for nature (including biodiversity, water), climate (including carbon sequestration and climate adaptation) and people (including livelihoods and community well-being). Monitor and evaluate your progress to implement these actions.
Shift business strategy and models. Adapt your company strategy and business model to “give back more than you take”, to restore ecosystems with collective measurable, reported and verified positive impacts, while also ensuring your negative impact footprint is as low as possible. Take inspiration from WBCSD’s Roadmap to Nature Positive and Sector Actions developed by BfN, WEF and WBCSD to inform your strategy. Embed nature at the core of your business; ensure that the value of biodiversity and climate impacts are weighed in critical decisions and that nature is integrated with your climate – and wider corporate strategies. Implement risk management procedures to address material risks identified and evaluated in your nature assessment. Identify actions to facilitate any nature-related opportunities. This could be through investment in transformational innovations and circular business models and products, such as buildings that absorb and break down pollutants. Engage in landscape-level and jurisdictional approaches for collaborative action to reduce impacts like deforestation and conversion, and produce positive changes through contextually appropriate investments in nature-based solutions. Divest from assets – including in your pension plans – that degrade and over-exploit nature and redirect resources towards sustainable use, resilience, restoration, and circularity. Monitor and evaluate your progress to implement these actions.
Encourage further business action – and thus the transformation of global economies – by making your methods and data open-source, and sharing your successes and challenges with companies that are starting their journey. Elevate the World Economic Forum’s 15 nature-positive transitions which could generate up to US$10.1 trillion in annual business value and create 395 million jobs by 2030.
Develop and publish a credible nature strategy and submit it for review as part of the ‘It’s Now for Nature’.
Collaborate, both along your value chain, and at a landscape seascape and river basin-level. Act systematically to apply the mitigation hierarchy beyond operations and engage with key stakeholders, including those in your corporate value chain, in the landscapes, seascapes and river basins where you operate or source, and in your sector. Downstream companies (those closer to consumers) should engage and support companies further upstream in their supply chains (those closer to raw extraction and production) to adopt lower impact practices, improve data collection abilities, and increase overall supply chain transparency. Consider how your business supports a just transition within your nature action.
Advocate for ambitious policies and initiatives
Sign up to the “Nature is Everyone’s Business” Call to Action, and support the Leaders’ Pledge for Nature.
Call on governments to adopt policies which create a stable operating environment and level playing field for business and contribute to key negotiations for nature.
Support specific business advocacy initiatives that contribute to reversing the loss of nature, e.g., business manifesto calling for a UN treaty on plastic pollution.
Embed nature within your corporate governance. Set out the ways in which the organization’s governance structure and decision-making functions take nature into account, including identifying any additional roles and resources that might be required to deliver the strategy and integrate performance on nature in your remuneration policy. Take steps to assign oversight of your nature strategy to your existing governance and management bodies to ensure there is accountability and responsibility for nature assessment and action within your business. Ensure your transformative actions are supported with policies, frameworks and procedures such that employees and wider stakeholders are aware of their role in delivering this strategy and it becomes embedded in BAU activities.
Publicly report material nature-related information throughout your journey
Seek out independent validation and verification to enhance credibility of actions. Seek independent validation and verification to assure the company’s processes used for value chain mapping, materiality assessments, prioritizing locations for action, gathering baseline data and setting targets. Consider aligning to relevant sector specific initiatives, certifications or accreditations.
Align reporting with major reporting standards. As much as possible, ensure alignment with existing reporting standards, both mandatory and voluntary, such as TNFD, ISSB, and the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), as well as with environmental data aggregators like CDP.
These high-level actions can be found in the following languages:
As you go through the steps, remember:
Re-visit your steps. The steps are iterative, and you can jump around depending on where you are already on your nature-positive journey.
Strive to be holistic. Integrate actions, targets and strategies across your company to tackle nature loss, climate change and social inequality together. Measure, monitor and publicly disclose your environmental performance and progress, and move towards comprehensive ESG disclosure.
Assign accountability and foster your corporate sustainability culture. Assign accountability for nature at the board level. Diffuse sustainability throughout the organization by engaging directly with employees, as well as all core functions such as finance, procurement and risk management, e.g. by taking a fit-for-purpose nature-based risk management approach (Fig. 8, Nature Risk Rising). Use the WBCSD’s Board director resources to modernize your company’s governance.
Make a plan. In order to close the commitment/implementation gap, make sure to translate your goals into a practical plan by setting milestones, identifying a team and allocating sufficient resources. For inspiration, read the CISL biodiversity strategy guide for the fashion industry.
Collaborate with others and don’t reinvent the wheel. Lean on the experience and expertise of others, and partner with NGOs, consultants, and other companies.
Don’t let the perfect be the enemy of the good. Be as ambitious as possible in your plans and actions, while being transparent and honest that there will always be improvements and adjustments along the way. This journey is an iterative one, and the “perfect methodology” might not yet exist.
For more information and inspiration, read UNEP's "Adapt to Survive: Business transformation in a time of uncertainty."
Disclaimer: These steps, in isolation, are not robust or detailed enough to constitute an endorsement or justification that your company is nature-positive.
Building on the high-level actions, Business for Nature, the World Business Council for Sustainable Development and the World Economic Forum have produced 12 sector-specific overviews that outline the key impacts and dependencies on nature and biodiversity and set out the priority actions that businesses in each sector should take now to credibly contribute to a nature-positive future.